This sounds too simple to justify a how-I, but don't be deceived: Windows Vista and upwards are tricky in the booting department.
First, the situation: I bought an Acer Aspire 5810T laptop that had Windows Vista Home Premium 64bit preinstalled, plus the usual junk. The laptop didn't have a recovery DVD but did have a recovery partition, which was just as well, since when I burned recovery DVDs, it turned out the laptop's DVD drive had a problem reading burned DVDs without the right drivers, which were clearly not present on the recovery DVDs. (I know this because they were present on the openSUSE installation DVD that I burned, since openSUSE installed. When the first Windows recovery DVD was in the drive, I just got repeated requests to insert a DVD.)
Also, I bought a touchscreen that needed Windows 7 to work. No problem, since the purchase included a Windows 7 update DVD (32bit, I later found out). With Windows versions, "update" rarely means update, so I should have installed W7 on a clean drive, but not to push my luck, I installed it over the existing Vista, which meant that Software Update, WinLocker and eRecovery no longer worked. (There is an update procedure to W7 for WinLocker which I didn't bother to follow; eRecovery is for reinstalling from the recovery partition.) Now before I did this update, I did remember to clean out all the junk and cut C: up into smaller partitions - a third primary partition to run Vista, and logical partitions for data - but I didn't think to clone the Vista partition to the third primary partition before I did the update. Although, given the booting problems of cloned Vista installs, that would only have saved me half the work...
Anyway, I now had the following primary partitions: a hidden recovery partition called "PQservice", a huge C: for Windows 7 plus Linux Mint in a container file (since, given the problems with reading burned DVDs, I couldn't boot the Linux Mint DVD and so had to install inside Windows), a much smaller C: for Vista, currently empty; and the logical partitions D: (data), E: (games), and F: (FATshare, this was a small FAT32 "buffer" partition for sharing files between Windows and Linux).
My plan: using the recovery partition, restore the original installation to the third primary partition, henceforth called Vista-C:, and clean it up. There were two problems with this: the recovery program no longer worked under Windows (but that could be fixed) and, more importantly, it insisted on overwriting not the third but the second primary partition, henceforth Big-C: (home to W7, but soon to accommodate Vista for a while). I found a text "SetActivePT.txt" on the recovery partition which pointed to a partition number 1, and changed this number to 2. No effect.
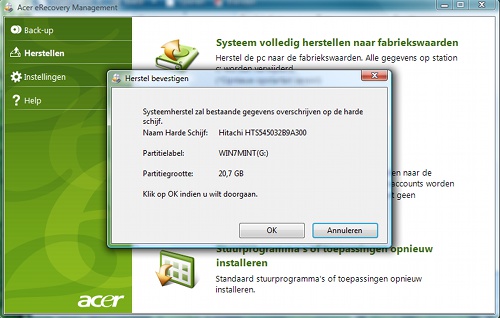
So a new plan was needed, which could not have been carried out without the already installed Linux: back up the contents of Big-C:, restore the original installation over Big-C:, copy the result to Vista-C: and then restore the old contents of Big-C:. This meant making two drive images. I had previously bought a 250GB USB drive, on which I'd hoped to gather all the MP3 files scattered over various systems, but which, I decided, would be a backup disk for the Acer laptop, despite being smaller than its 320BG harddisk; if I only used it for the Windows partitions, that would be plenty of space. It was formatted as follows: a 1GB NTFS partition containing a copy of the MBR made with the hex editor HxD (and anything else boot-related that turns up), then a huge ext2 partition, the size of all primary partitions together, for the primary partition images, and then a huge NTFS partition with directories D and E, and finally an 8GB FAT32 partition for F. As this suggests, the primary partitions would be backed up as images, while the logical partitions would just have their files backed up.
The partition for the images was in the ext2 format because the imaging was done under Linux. For older computers, my imaging program of choice had been PowerQuest Disk Image II, offered as a freebie by a computer magazine I was subscribed to, but no longer adequate for modern drive sizes and partition formats. So after trying some Windows freeware, which tried to copy image files to unallocated space and didn't like the USB drive, I settled on the KDE Partition Manager in openSUSE 11.3, under the Gnome desktop.
(The following steps were worked out by trial and error, so there was much more imaging and restoring and switching between Windows and Linux than is described below.)
Step 0 was already done: partition
harddisk so that there is now a second primary partition for Vista. (Optionally,
kick oneself for installing Windows 7 before getting that second Vista partition
done and working. Or for putting W7 on the second partition instead of the
third, where eRecovery would have left it alone.)
Step 1: prepare the USB drive. Log into SUSE Linux
as root, start KDE Partition Manager, start Disk Utility to unmount the USB
drive, partition as outlined above using the Partition Manager, remount. (I
finished this step after step 2, that is: I made a big ext2 partition, imaged
the primary partitions to it to see how much space they would take, then used
the remaining space for the backup partitions for D:, E: and F:.)
Step 2: now the primary partitions will be imaged
to the USB drive. Using the Disk Utility, remount the USB drive. Unmount Big-C:
(this can be done a number of ways, the easiest way is inside the KDE Partition
Manager itself). Then make images using the backup/restore feature of KDE
Partition Manager. I made images of the recovery partition, Big-C: and Vista-C:,
and copied them in that order, including all sectors. Some imaging software
allows the empty sectors to be skipped, reducing image file size, but I wanted
the image files to be always the same size, so that I could overwrite them with
future backups without worrying about disk fragmentation or suddenly running out
of disk space. As a test, I imaged and then restored Big-C:; all the files were
in place, and Vista-C: was still empty.
Step 3: use GRUB to make the recovery partition
available. Before doing this, I opened the harddisk in a nifty hex editor called
HxD, which opens disks and partitions as well as files, and copied sector 0, the
Master Boot Record, to a file on the USB drive, as I was worried that the
recovery would overwrite the MBR as well as all of the harddisk. (It doesn't. It
picks the first primary partition after itself, and limits its operations to
that partition.) This is because even if I manage to get eRecovery working, it
will attempt to reboot into the recovery partition, but instead will start GRUB,
which has no entry for the recovery partition. Once the GRUB menu does have that
entry, I can choose "PQservice" and continue the recovery process.
Under Linux, go to /boot/grub and, as root, open a file called "menu.lst".
Under the other entries, add:
To those unfamiliar with GRUB, "(hd0,0)" means the first harddisk and its
first partition, as it starts counting at 0. So "(hd0,1)" means the second
partition on the first harddisk, and so on. I'm not sure the second two unhides
are even necessary, but better safe than sorry.
You can remove this entry once it is no longer needed, but I never scroll
down that far when booting anyway, and if not chosen as part of running
eRecovery it will simply try to start its partition, give up, and reboot, so
there's no harm in keeping it. All the unhide commands do mean that the C:
partitions should rehide it on booting, so I changed the existing Windows boot
entries to the following, to make sure only one primary partition was visible at
one time:
This hiding got me in trouble once Vista was finally on its own partition,
but let's not run ahead. (Incidentally, if used by eRecovery, the partition will
re-hide itself when done.)
Step 4: put back the eRecovery program files that
were wiped in the update to W7. Just as the recovery files are not on DVD but on
a hidden partition, the drivers and applications one would expect to find on a
separate CD are in the directory C:\Acer. The program to run is
"C:\Acer\Preload\Autorun\APP\eRy\setup.exe".
Step 5: start eRecovery. Don't bother looking in
the Start Menu, just go to "C:\Program Files\Acer\Acer eRecovery Management" and
click on "eRecoveryUI.exe". (If working under Vista, right-click and choose "Run
as Administrator"; HxD when used for disk editing also has to be started in this
way. W7 doesn't need this.) Choose a recovery option. I initially chose the
second option - recover the OS only - and was rebooted (using GRUB's new entry)
into an interface which looked as if it ran under DOS. It told me it couldn't
find my user data (that's right, I'd used tweaks to move as many user
directories as possible to D:) and advised what had been option 1: a total
system restore. Okay, here goes: Big-C: was wiped and filled with the original
installation, which, on restarting, went through the usual rigmarole of a
freshly installed Windows: disk check, setting first-time preferences and
creating a user account. Even with junk included, it took up only half the space
of Win7 plus Linux Mint. In fact, its contents would now fit in Vista-C:.
Step 6 is something -
three things - I should have done straight away. Vista-C: is, for the moment, an
empty NTFS partition. Open it, read-only, in HxD. The first thing you see is the
contents of sector 0, the partition's boot sector. This is called the Partition
Boot Sector, Partition Boot Record, Volume Boot Sector or Volume Boot Record;
analogous to the MBR, I will call it Volume Boot Record or VBR, as in Vista and
upwards it is 16 sectors big, although only the first sector is needed to boot.
(What the rest of the record stores is a mystery to me, but it appears that
sector 15 logs something.) Anyway, the sector is laid out in rows of 16 bytes,
starting with row 0. I should have copied the last four bytes of row 1 and the
last eight bytes of row 4 to a text file. Next, in Vista on Big-C:, I should
have generalized the BCD with "bcdedit.exe" (more on that below),
run RegEdit and deleted the key "HKLM\SYSTEM\MountedDevices".
Step 7: clone Big-C: to Vista-C:, so that the
Windows 7 backup can be restored to Big-C:, and Vista-C: can be cleaned up. Of
course, if it was that simple, this how-I would not have been written.
The cloning is fairly simple, though. Boot back into Linux as root. Using the
KDE Partition Manager, shrink Big-C: to exactly the same size as Vista-C:. (For
me, this shrinking wouldn't work with KDE Partition Manager, and did work but
produced disk geometry errors with ntfsresize, so I re-ran eRecovery in Vista
from the shrunk partition, expecting the reformatting and reinstall to solve any
formatting problems, which they did, so now the partition was ready for imaging.
It appears that Vista and upwards have a certain partitioning style that other
OSes don't always know how to handle.) Then image Big-C: to the USB drive as the
Vista-C: image, letting the image overwrite any existing backed-up Vista-C:
image file, and restore this image file to Vista-C:. Basically, Big-C: has been
copied to Vista-C: through backup and restore.
Step 8 is something else I should have done the
first time, and before booting the new Vista: while still in Linux, copy
the generalized BCD from Big-C:\boot to Vista-C:\boot. Then, in Vista on Big-C:
(don't start Vista-C: yet!) open partition Vista-C: in HxD, not read-only
this time, and edit the VBR: change the four last bytes in row 1 and and the
eight last bytes in row 4 to the values noted in step 6.
If steps 6 and 8 are done, Vista-C: will boot flawlessly to its own desktop,
and can be cleaned up and backed up to an image, while the W7 image can be
restored to Big-C:.
Of course, I hadn't followed these steps, and as such faced the
exasperating situation experienced by most users who try to clone their Vista,
either to move it or to test a backup image they made: Vista will not boot
because its boot manager is missing. Or it will boot, but strangely enough to
the partition it was cloned off. Or it will boot off its own partition, but
stubbornly insist that its drive letter is G: (or anything other than C:) which
plays merry hell with Windows. This was my first experience with BCD (the Boot
Configuration Data file), and the Vista VBR. I wrote up my trials to help anyone
else stuck in this confounding situation, and damn Microsoft for being
"user-friendly" by covering up the workings of its latest OSes. Here, ladies and
gentlemen, is how I did it (wrong).
To sum up: I had copied Big-C: to image, restored over Big-C:, resized
Big-C:, copied Big-C: to a "Vista-C:" image, and restored this image to
Vista-C:. So in GRUB, I booted the Vista-C: partition, expecting it to boot, as
the DOS-based Windowses would have done. Instead, there was a complaint about a
missing AUTOCHK.EXE, followed by a reboot.
So I booted Big-C: instead, which was fine and gave no indication of what was
wrong. Now, in the old Windowses I'm used to, "boot partition X" means that
partition X uses the boot programs on itself to boot itself and load its own
Windows; any instruction on where to find things is relative. In Windows Vista
and upwards, the "system" partition contains the BCD, a catalogue of bootable
partitions, that specifies which boot entry should use which partition. So, if I
booted Big-C:, its BCD told it to boot off the second primary partition. And if
I booted Vista-C:, the third primary partition, which had exactly the same BCD,
its BCD would tell it to boot off the second primary partition, which was
hidden, as set in GRUB's menu file. So there was nothing to boot.
I tested this by altering GRUB's menu file (/boot/grub/menu.lst) so that
Big-C: was no longer hidden when I booted Vista-C:. And indeed: if I chose
Big-C:, then Big-C: was booted. If I chose Vista-C:, then Big-C: was booted.
Since the two installs were identical, I chose a particular desktop wallpaper
and put an empty file called "win7.txt" on the Big-C: desktop so I would always
know what partition had booted. And I saw that wallpaper and file on every boot.
Well, you may think, the solution is simple! Edit the third partition's BCD to
point at the third partition! There is currently no Linux tool for doing this.
I'm stuck with either Windows' own utility BCDedit
(\windows\system32\bcdedit.exe) or the shareware BCDeasy. The latter option had
an alternative which I used instead: Visual BCD
Editor, a freeware tool that didn't work as reliably as BCDedit when
generalizing the BCD, but that does give clear insight into the BCD's structure.
My first problem is that I couldn't get BCDedit to open a BCD! It complained
that it couldn't open an "active file". Used to Windows 7, not to Vista which is
constantly yammering for an administrator to do things, I didn't know yet that
programs in Vista are best run by right-clicking on the executable and choosing
"run as administrator". This makes the security advantage of an administrator
user pretty much moot, which is why it was scrapped in Windows 7. Anyway, a
quick way is to type "cmd" in the Start Menu search field, which brings up
"CMD.EXE", which can then be right-clicked on to open a DOS prompt where I can
type in the command "bcdedit /enum /v" to see what the heck is going on.
The second problem is that I didn't know how to access the BCD on Vista-C:,
since I couldn't boot Vista-C:. After some searching and reading the cryptic
help information supplied by BCDedit, I found that any BCD on any partition
could be accessed as long as the partition itself could be accessed. So, in
GRUB's menu file, I also unhid Vista-C: when booting from Big-C:, and then, in
Big-C: where Vista-C: showed up as G:, used
Having discovered how to edit either BCD with BCDedit and reading something
about generalizing the BCD, I thought that would be the solution.
Generalizing the BCD: this information was copied from a
site on dual booting and multibooting
Vista. Possibly due to the number of people who are fond of their older
Windowses, Vista and upwards support multiboot in a nefarious way; you can
install Windows XP and Vista on different partitions, but they'll still both
start from the same partition, namely the one where the file "bootmgr" and the
BCD is found. Vista has no qualms about infiltrating the XP partition to plant
its own booting files there, and when the owner decides to stick with Vista and
delete the XP partition, Vista will no longer start. This site is about genuine
multibooting: each OS with its own startup files on its own partition. One of
its sections is about cloning Vista. Usually, if Vista is installed again in a
second partition - to have a "clean" and "test" installation side by side, for
instance - it will again conspire with the first Vista to boot off the same BCD.
The idea behind cloning is that two partitions are made, Vista is installed on
the first, then the first partition is copied to the second. This way, neither
Vista installation has anything to do with the other, and they can be booted
with an external boot manager, or either's BCD can be edited to add an entry to
boot the other installation, but the essential thing is, both partitions use
their own BCD.
The problem I had, as I later gleaned from the Starman PC Ministry's page on the NTFS volume
sector, is that the BCD refers to a partition by its volume ID, which is
found in its boot sector and should be unique for each partition/volume. As you
can guess, if a partition is copied by making an image file of it, that includes
the boot sector, and writing it to a new partition means there are two
partitions with the same volume ID. This is why steps 6 and
8 are needed. But I assume the Vista-cloning page from the dual/multibooter
site referred to the copying of files only, which means that the BCDs on both
partitions are the same, but the partitions' boot sectors are different. In
which case, generalizing the BCD will simply work.
The BCD on a partition is found in directory "\boot", and BCDedit is found in
"\Windows\system32\". In the example below, C: and D: are two primary partitions
with Vista on them, and I'm working from the first one. To generalize the BCD on
the partition that is booted from, these are the commands to type at the prompt:
Now, while still booted from C:, I want to generalize the BCD on D:, for
which "current" has to be replaced by "default":
These instructions include the memory test setting, but exclude the "resume
object" setting that says where "hiberfil.sys" is found to wake the computer
from hibernation. This setting may or may not be in a particular BCD. It was in
mine, and I tried setting this to "boot" in Visual BCD Editor, but that wouldn't
work. So my "generalized" BCD isn't completely general and still needs one line
edited with Visual BCD Editor (I wouldn't even know how to do this with BCDedit
- something with "/osloader resume", I assume) after being copied to a
partition.
Some time later, I found out how to set "resume object" to "boot" in the
Visual BCD Editor, see picture below:
(If you read this as part of the "steps" section, click here
to return to that section.)
In my case, this didn't seem to work, because I didn't know yet about steps 6 and 8. After that, it did work, and I copied the
generalized BCD to the same backup partition where I keep a copy of the MBR.
To continue with what happened before that: since generalizing the BCD didn't
work, and I did want to boot Vista-C: so I could edit its BCD from its own
partition (this was not necessary, but I thought it was) I first unhid both
partitions from each other by editing the GRUB menu file:
Now, Vista-C: showed up as G: when booting Big-C:, and vice versa. Then, I
added a boot entry for Vista-C: in Big-C:'s BCD with Visual BCD Editor. Now,
when I rebooted and chose "Win7Mint" in GRUB, I was presented with two choices:
continue to boot from Big-C:, or boot "Vista" on Vista-C:. But... I was still
booting from Big-C:. The boot menu let me boot the third partition, but looked
for Windows on the second partition. Yes, Vista-C: was "drive C:", but that
meant that the Windows I'd booted into was on drive G:, so all sorts of programs
didn't work. The problem seemed to be that even when booting Vista-C:, Big-C:
was considered the active and boot partition. Windows Disk Management told me:
A bit of explanation: the system partition is the one whose BCD is used. The
boot partition is the one that Windows is supposed to boot off, although in
practice this is also influenced by which partition is active. Page file and
crash dump are the files written in preferably the active partition's root as
hibernation file (hiberfil.sys) or when the computer crashes.
There had to be a way to shift the "boot" and "active" flags from G: to C:,
as GRUB's "makeactive" didn't do the trick. And it had to be done before Windows
started (off the wrong partition).
Oh, the trouble I put myself through. Trying to find the GUIDs (unique
identifiers) of the BCD objects and changing them for the different boot
options. Hiding a partition or the BCD on a partition. Repairing the BCDs and
creating new ones. Carefully attempting the fix "bootsect.zip", which was only
intended for problems caused by switching beween Vista and XP. Saving all 16
sectors of the "clean" VBR after a format and comparing them to the 16 sectors
of the VBR after putting back the image file. Altering bytes in the VBR when I
saw that C: and G: had exactly the same volume ID (well, I was on the right
track there). Going into Recovery Mode in an attempt to find some basic drive
letter setting.
In the end, after much surfing and trying things, I reformatted Vista-C:,
noted the 4 and 8 bytes, copied the saved Vista image over it, and changed the 4
and 8 bytes back. And that's how I belatedly carried out steps 6 and 8. Except
for the registry editing, that came later still.
This, in combination with the generalized BCD, worked. Both Vista-C: and
Big-C: now used their own BCD and their own Windows executables, so I didn't
have to boot Vista-C: via Big-C: any more. The trouble was, Vista-C: still
considered itself partition G:, and so referred to Big-C: ("C:") for Windows and
user settings.
This is because unlike the old Windowses which reletter drives and partitions
at every boot, the new Windowses give a partition one letter and stick with it,
booting order and active partitions be damned. And since this time the fault lay
with Windows, it could only be solved through RegEdit.
The solution to such partition misjudgements, I found on the Internet, is to
delete everything under HKLM\SYSTEM\MountedDevices. Anyone who has used RegEdit
knows that HKLM stands for HKey_Local_Machine, but not everyone may know that
all HKLM keys and values are stored in a file called SYSTEM in
\Windows\System32\Config. This is useful to know when it isn't possible to empty
this key in RegEdit directly, for instance, when RegEdit won't work because the
Windows partition isn't the C: partition. Therefore, I had to boot Big-C:, start
RegEdit, and load the "hive" (or "component", as the Dutch RegEdit calls it)
G:\Windows\System32\Config\SYSTEM under a random name. I picked "boojah" because
it was the most articulate thing I could say after days and nights of fighting
with this laptop.
Under "boojah", I found "MountedDevices" and deleted what was under it. I
then unloaded the hive, thereby saving SYSTEM on Vista-C:, before deleting it
from Big-C:'s registry.
Rebooting to Vista-C:, I saw that the last hurdle had been cleared: when
booted, partition Vista-C: called itself C:.
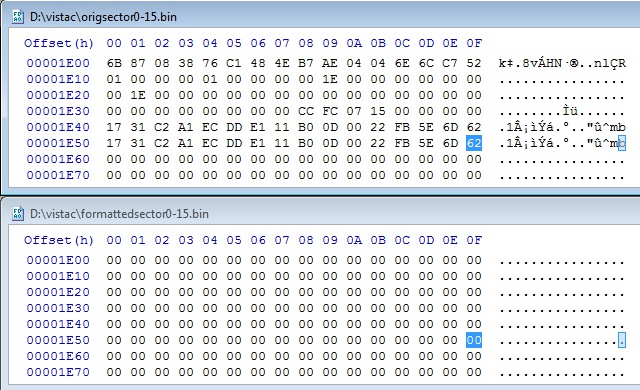
As an afterthought, a screenshot of the differences I found in the last
sector when comparing VBRs between a partition with Vista installed, and the
same partition cleanly formatted. This is how I located the volume ID bytes that
needed changing in the first sector, but what the bytes below are for, I have no
idea. Maybe I'll find out some day.
Finally, something about Acer's recovery partition. This is a
notebook-specific, hidden partition of about 10 Gb at the beginning of the
harddisk, with the volume label PQSERVICE. It is a FAT partition, normally
hidden, but it showed up under Zenwalk Linux in read/write mode, which allowed
me to poke around a bit until I made the wise decision of making it read-only in
the fstab.
Although it can't be booted like a normal bootable partition, pressing
Alt-F10 makes the notebook boot this partition, which then automatically
restores the original installation on the first primary partition after it. The
code that makes this happen is in the MBR, so if you're like me and you install
Linux and put GRUB in the MBR (the default location), the magic
restore-by-keypress is gone and the only way to use this partition at all is to
give it a place in the GRUB menu, as described higher up. If you delete or
format the partition, the laptop's system recovery ability is gone, despite all
and any anguished posts to computer forums. Apparently, recovery disks can be
bought, somewhere, at a high price.
When it boots, which it should do automatically when normal startup fails, it
does so in one of two modes: recovery, in which the second primary partition is
simply overwritten, or repair, where you get a menu, but the bottom-most
"recovery" menu item does nothing. This is supposed to be the Windows Repair
Console, another good reason for not deleting this partition to free up space.
On PQSERVICE there is a text file "SetActivePT.txt", which I altered, and a
text file "p1.dat" containing only the text "PArtition 1" [sic] of which I made
a copy "p2.dat" containing the text "PArtition 2". This didn't help, the
recovery program kept choosing the second primary partition, and if this
partition was hidden, gave the error message "FAIL to get disk 0 partition 2
drive letter". There is also a WIM (Windows Image) file, and several BCDs and
NAPP logfiles. The BCDs will boot the WIM and its Windows Repair Console from a
RAM disk, which is why the files on the partition are different from the files I
see when going to the prompt in recovery mode. Someone with more knowledge would
be able to change the BCDs to grab the third rather than the second primary
partition for restoring.
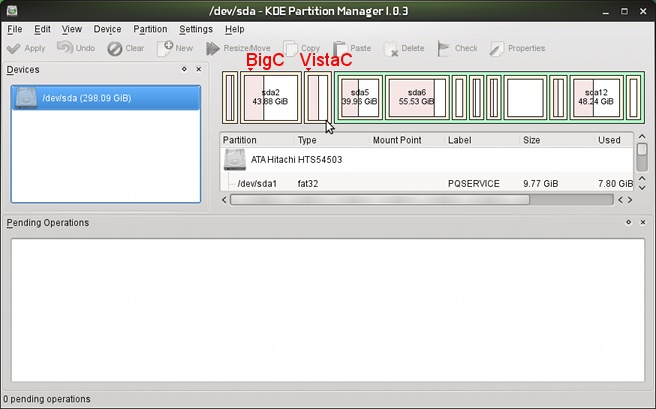
A tiny recovery partition, a huge Windows 7 partition and some space for
Vista.

I added Disk Utility to the Favourites menu during this operation.
title PQservice
unhide (hd0,0)
unhide (hd0,1)
unhide (hd0,2)
rootnoverify (hd0,0)
makeactive
chainloader +1
title Win7_Mint
unhide (hd0,1)
hide (hd0,2)
hide (hd0,0)
rootnoverify (hd0,1)
makeactive
chainloader +1
title Vista
unhide (hd0,2)
hide (hd0,1)
hide (hd0,0)
rootnoverify (hd0,2)
makeactive
chainloader +1
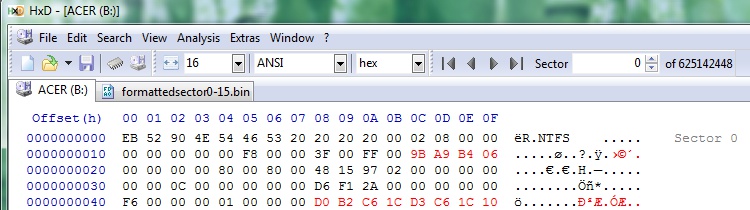
The bytes that need to be copied and put back in later.

Sizing Big-C: down to Vista-C:.
"bcdedit /store G:\boot\bcd /enum /v".
The "/store" flag specifies a drive and path, and is very useful when you
don't know which BCD is "active", ie. loaded into memory and edited by default
if no store is specified. Editing the wrong BCD can make a system unbootable and
in need of a System Recovery disk. Acer's hidden partition PQservice also acts
as System Recovery disk, but is still started from the BCD, so it's best to
avoid mistakes.
bcdedit /store C:\boot\bcd /set {current} osdevice boot
bcdedit /store C:\boot\bcd /set {current} device boot
bcdedit /store C:\boot\bcd /set {bootmgr} device boot
bcdedit /store C:\boot\bcd /set {memdiag} device boot
bcdedit /store D:\boot\bcd /set {default} osdevice boot
bcdedit /store D:\boot\bcd /set {default} device boot
bcdedit /store D:\boot\bcd /set {bootmgr} device boot
bcdedit /store D:\boot\bcd /set {memdiag} device boot
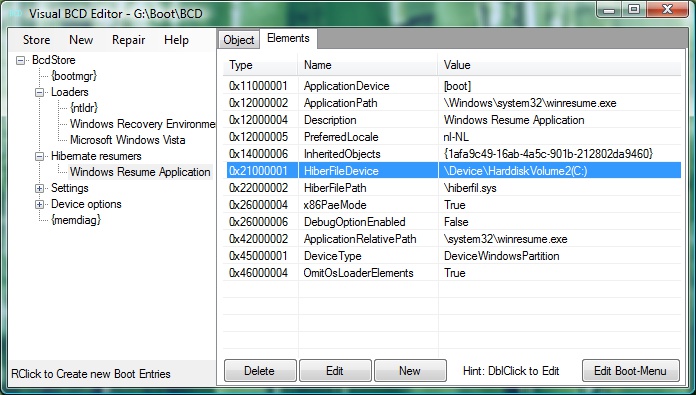
A screenshot of Visual BCD Editor showing the HiberFileDevice line.

Choose the type "BootDevice", then, optionally, disk "[boot]".
title Win7_Mint
unhide (hd0,1)
unhide (hd0,2)
hide (hd0,0)
rootnoverify (hd0,1)
makeactive
chainloader +1
title Vista
unhide (hd0,2)
unhide (hd0,1)
hide (hd0,0)
rootnoverify (hd0,2)
makeactive
chainloader +1
Schijfbeheer:
C: Systeem, Primaire Partitie
G: Opstarten, Wisselbestand, Actief, Crashdump, Primaire Partitie
Translation:
Disk Management:
C: System, Primary Partition
G: Boot, Page File, Active, Crash Dump, Primary Partition

Let's show that again.
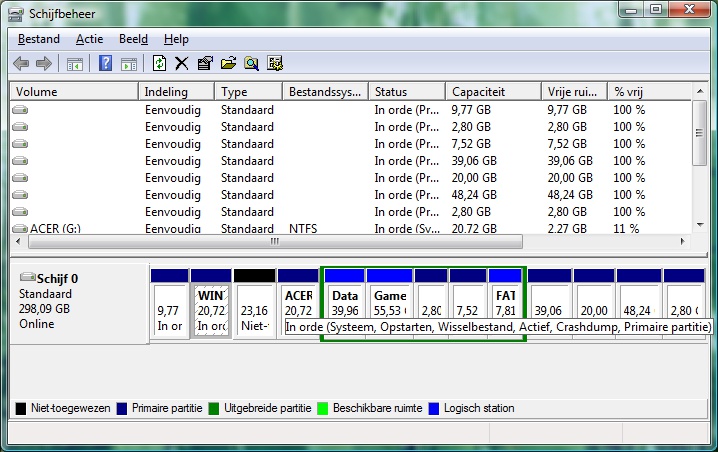
Everything's there, but on the wrong partition.
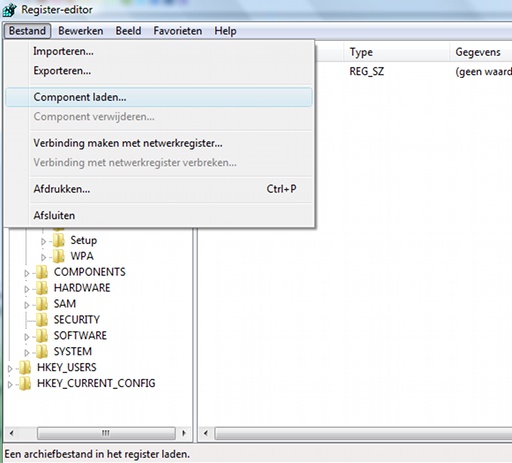
Importing Vista-C:'s SYSTEM in Big-C:'s registry for off-site editing.
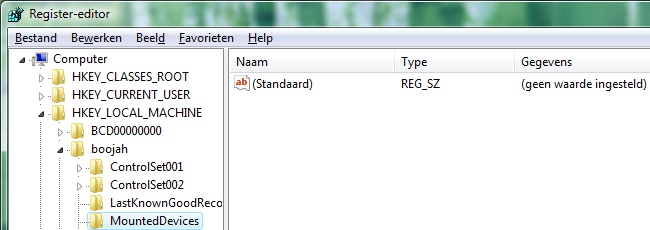
The offending key, now with nothing under it.
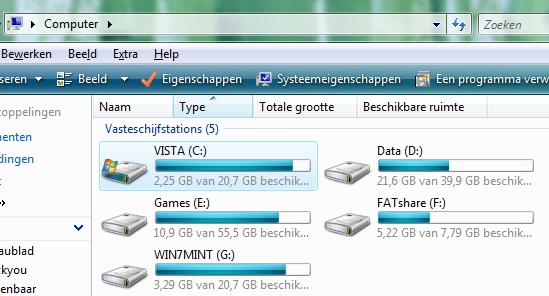
It works. Get the champagne.
What does this do?